Kerberos 101
Tags: active-directory, kerberosKerberos Series: Kerberos 101
This post is part-3 of the Auror Project hosted by Sudarshan Pisupati.
Table of Contents
What is Kerberos
How does authentication through Kerberos work
Kerberos Flows
- Logon Ticket Flow
- Service Ticket Flow
Kerberos Flows in Action
- User login to Machine-B
- User tries to access file server
Final Thoughts
What is Kerberos
Kerberos is a network authentication protocol developed by Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). The protocol was named after “Cerberus”, the three headed dog in Greek Mythology.
Kerberos is designed for a client-server model and provide secure authentication over a network. Windows 2000 and later versions use Kerberos as the default authentication method.
How does authentication through Kerberos work
Authentication through Kerberos happens through a Key Distribution Center(KDC) which is a service running on the Active Directory(AD) Domain Controllers(DC).
The main components in the Kerberos Authentication Process are
Authentication Service(AS) - Authenticate users when they attempt to access a service (example: user trying to access file server)
Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) - is the Kerberos ticket for the Ticket Granting Service (runs on the KDC) and is encrypted using the KDC key
Ticket Granting Service (TGS) - When the user’s TGT is presented to the Domain Controller (DC) it determines if the TGT is valid and issues a resource access ticket (TGS) which can be used to access the target resource (example: File server)
Every service in the Kerberos realm has a Service Principal Name (SPN) and every user in the AD domain will have a User Principal Name (UPN). For any service the SPN can be configured using the setSPN command.
| Service | Domain | SPN |
|---|
| File server | acme.corp | cifs/host1.acme.corp |
Kerberos Flows
There are two important flows that we discuss here
- Logon Ticket flow
- Service Ticket flow
The sequence diagram tries to provide an overview of both the flows
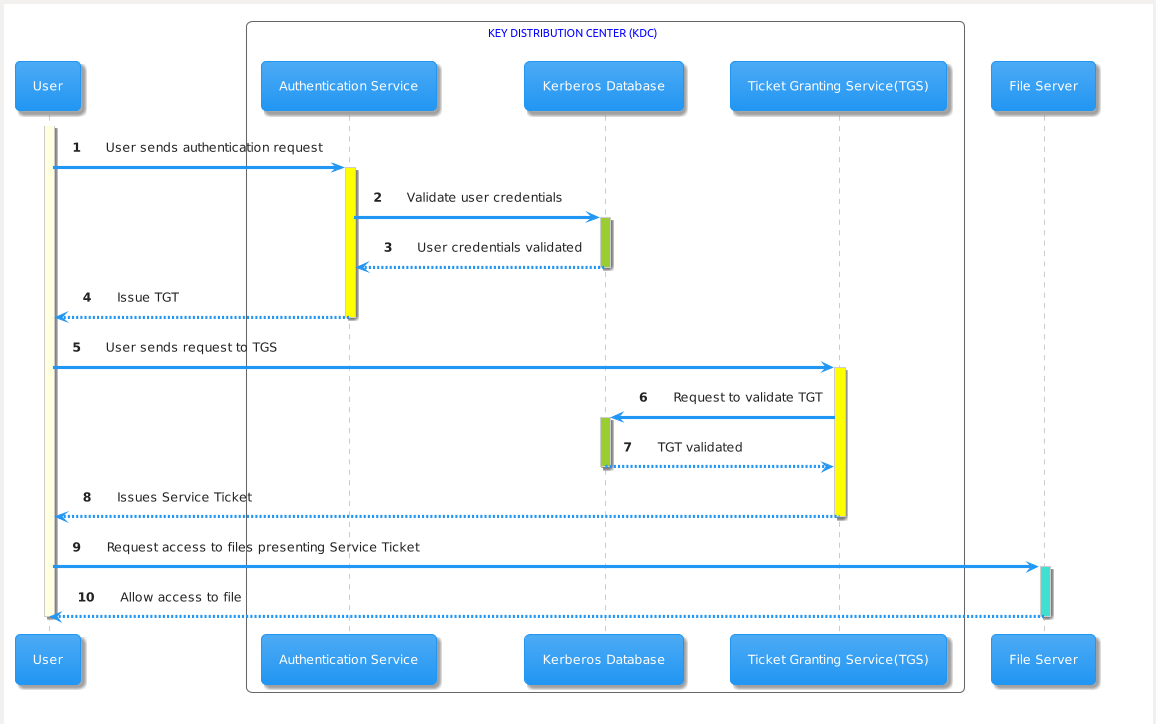
Logon Ticket flow (TGT Flow)
- User logs into a computer that is joined to the domain “acme.corp” using the Active Directory username and password.
- The computer creates a hash of the password when the user is logged in successfully.
- Kerberos authentication is initiated by sending the PREAUTH ( timestamp encrypted with the hash of the password)
- The user account ([email protected]) requests a TGT with the PREAUTH data. This process is also known as Authentication Service Request or AS-REQ
- The Key Distribution Center (KDC) validates the PREAUTH data and issues a Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT). This process is also known as Authentication Service Response or AS-REP
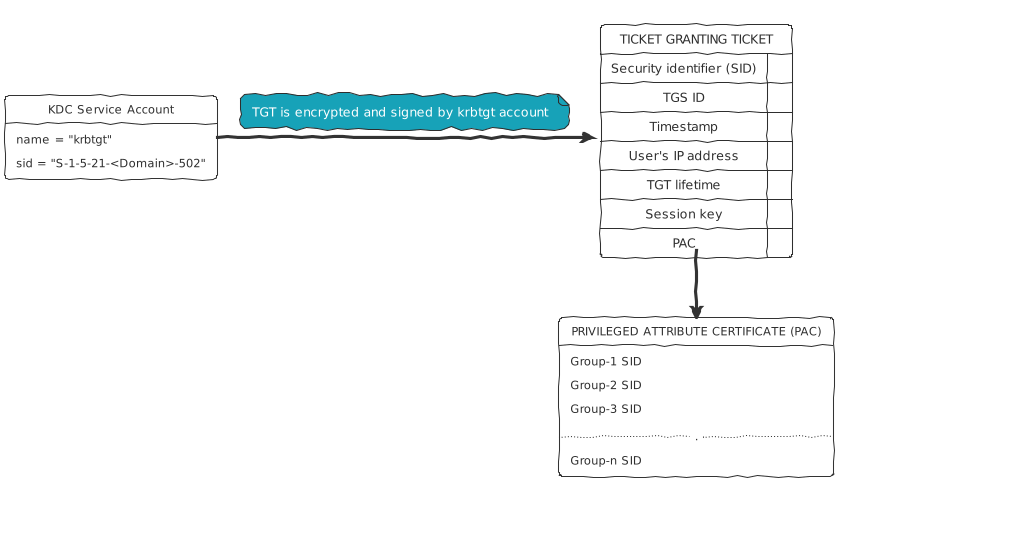
- The TGT contains Privileged Attribute Certificate (PAC) which has the list of security groups of the user.
- The TGT is signed and encrypted by the kerberos service account “krbtgt” of the domain.
- The contents of the TGT can be read only by the “krbtgt” service account which will be used as a reference during the kerberos attacks discussed later.
Service Ticket flow (TGS flow)
In this flow , the TGT will be used as a proof of identity while requesting access to a resource
- When the user attempts to access a fileserver in the domain,the TGT is presented to the KDC requesting a resource access ticket (TGS). This process is also known as TGS-REQ
- The Domain Controller determines if the TGT is valid.
- If the TGT is valid,it generates a service ticket (TGS). The service ticket is encrypted using secret key of the service and the session key generated by TGS. This process is also known as TGS-REP
- The user’s computer sends the user’s service ticket (TGS) to the file server (CIFS service).
- The resource service(CIFS) validates the TGS by decrypting the TGS component encrypted using the service’s session key.
- The resource service may send the TGS to KDC to validate the user’s group membership present in the PAC.
- The service review’s the user’s group membership and determines the level of access that can be provided to the user.
- It then allows the user to access the resource (file server).
Kerberos Flows in Action
To view these flows in action
We will use the Active Directory lab we have configured earlier. I have also configured a File server running on the Domain Controller (Machine-A).
We will configure the Service Principal Name for the File server that we have configured.
Below given is the command to set SPN for the file server
setspn -s cifs/aurordc.auror.local aurordc
PS C:\Users\Administrator> setspn -s cifs/aurordc.auror.local aurordc
Checking domain DC=auror,DC=local
Registering ServicePrincipalNames for CN=AURORDC,OU=Domain Controllers,DC=auror,DC=local
cifs/aurordc.auror.local
Updated object
- To verify if the SPN is added successfully , we can run the
setSPN -L command to list the SPN’s added.
NOTE: The SPN list has been truncated and only the file server we added is presented in the output below.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> setspn -L aurordc
Registered ServicePrincipalNames for CN=AURORDC,OU=Domain Controllers,DC=auror,DC=local:
cifs/aurordc.auror.local
User Alice (auror\alice) will login to Machine-B which is joined to Domain (auror.local)
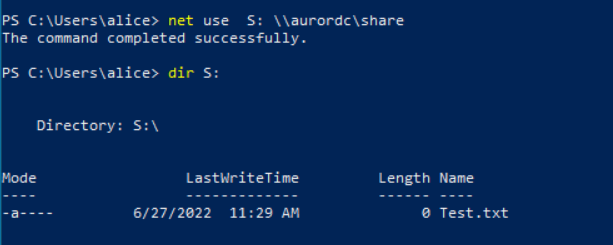
User Alice will then map the file share to S:\ drive.
User Alice will access S:\ drive.
User login to Machine-B
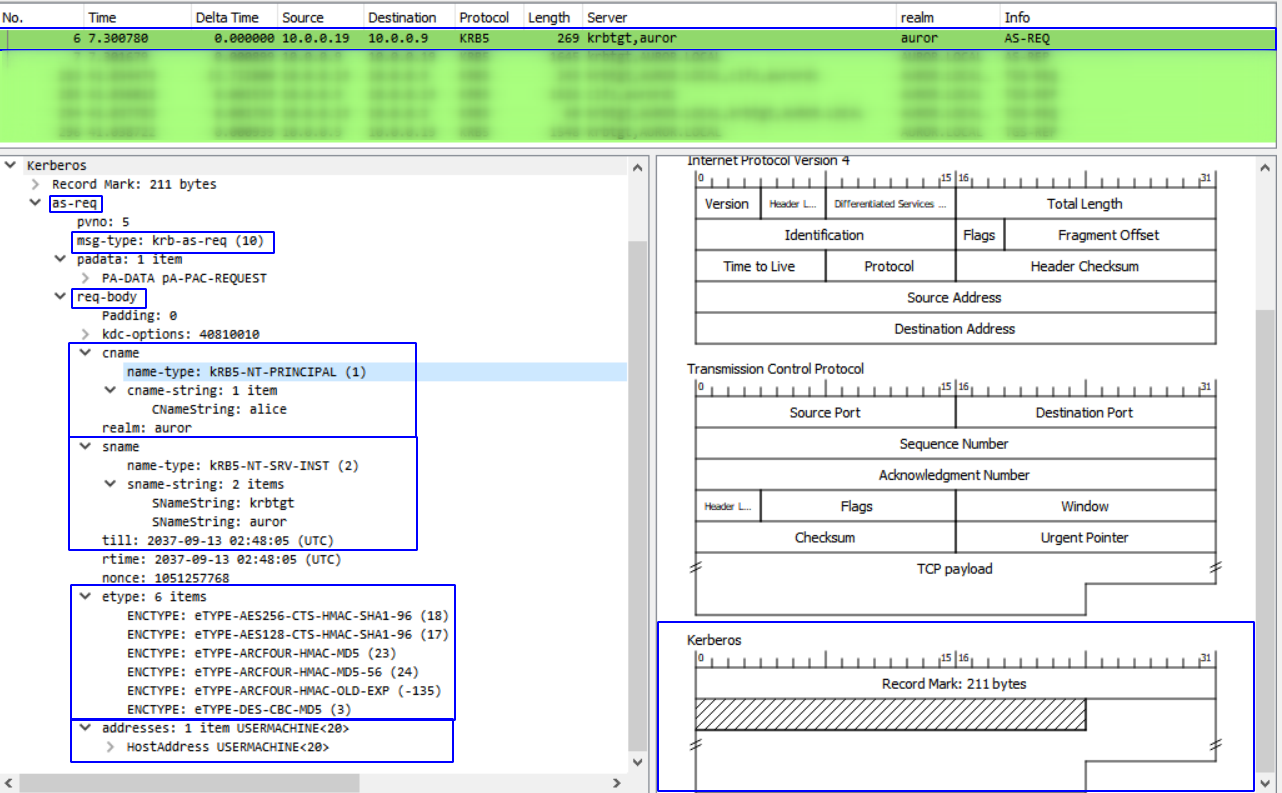
- When the user login to Machine-B, the client sends an AS-REQ to the Authentication Server we can find the below packets when analyzed through Wireshark
| Field name | Content |
|---|
| pdata | It is called “Pre-Authentication Data”. The client inserts a time stamp here and encrypt it with the client password to avoid replay attacks |
| cname | Client (user) name to be authenticated |
| realm | Domain Name |
| SName | Service Name being requested |
| till | expiration time of the ticket being requested |
| etype | encryption type the client supports |
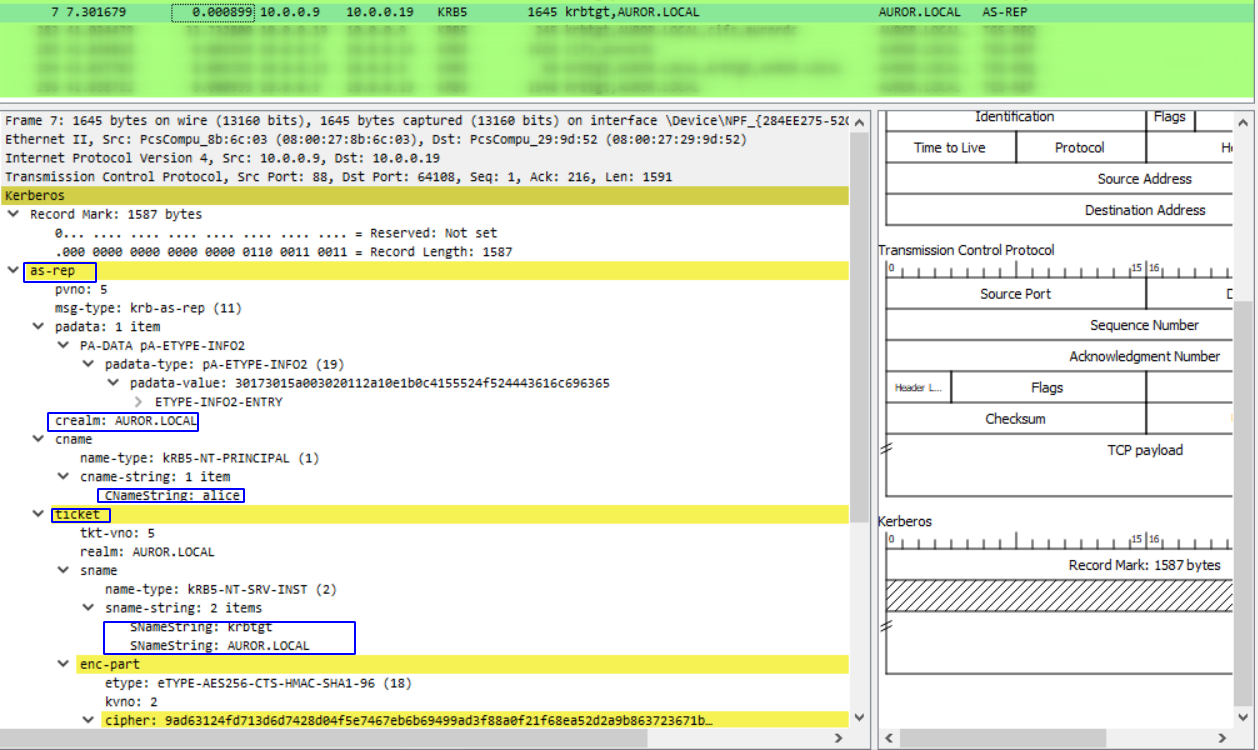
- The Authentication server responds with AS-REP packet to the client. The AS-REP packet contains a TGT (which is encrypted by krbtgt) and a session key
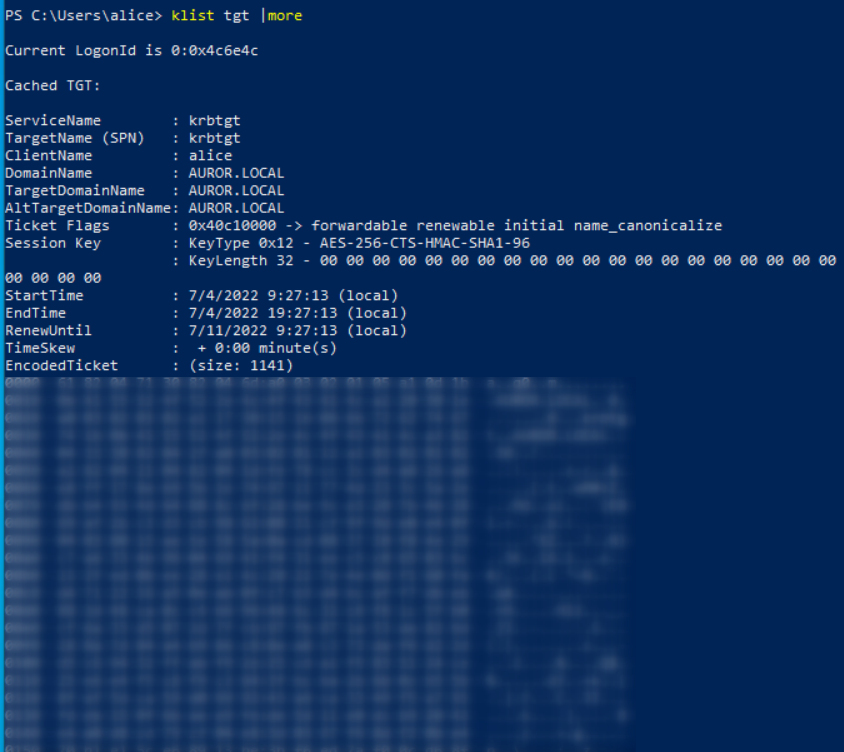
- We can view the TGT cached on Machine-B by issuing the command
klist tgt | more in Powershell
User tries to access file-server
- User tries to map the file server to a drive on Machine-B and access the contents of the drive.
- During this process the client makes a TGS-REQ to the TGS. The request contains the encrypted TGT and an authenticator using the client’s session key.
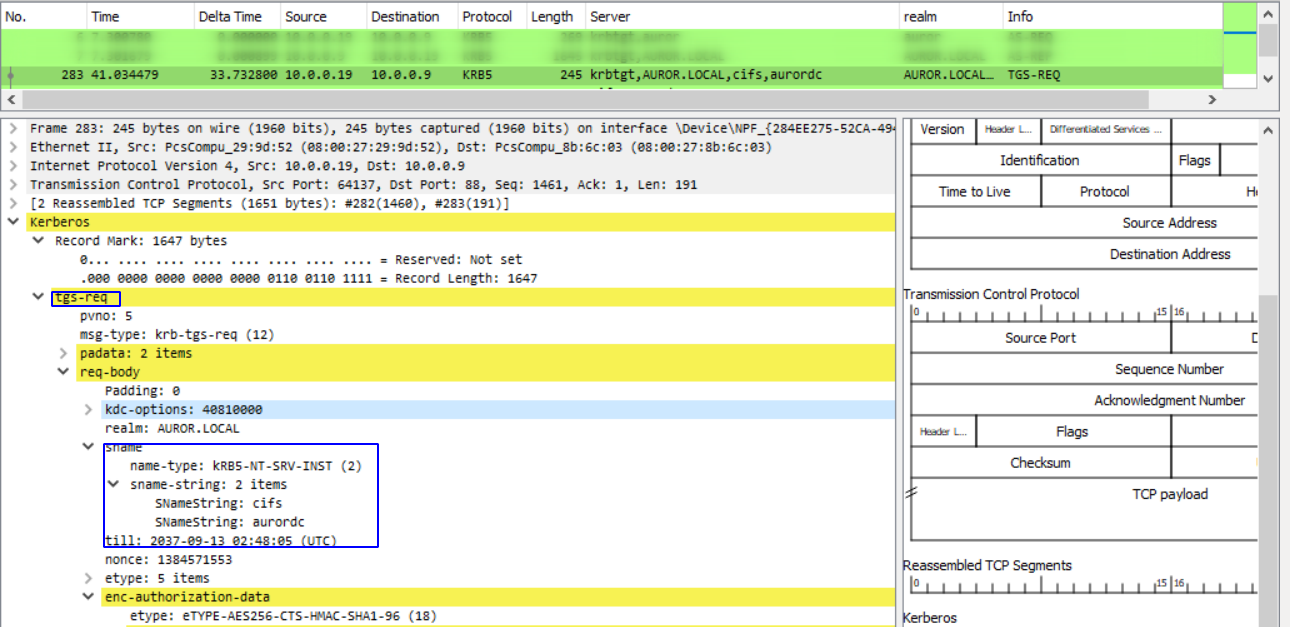
Through this request, the client is asking the server for a service ticket.
When the TGS receives this request it decrypts the TGT using the master key (encrypted by krbtgt)
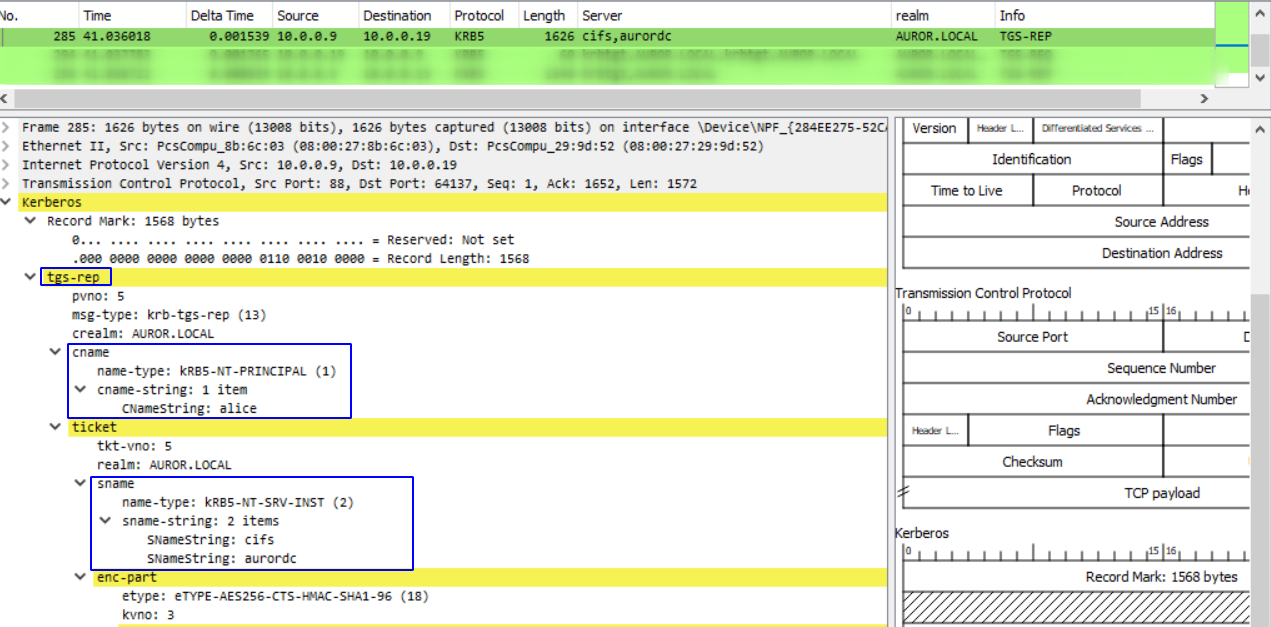
The TGS construcs a service ticket and encrypts it with another secret key which is shared between TGS and the File Server.
The service ticket includes information such as service name, client id, expiry date, a new session key, the client’s address etc.
Final Thoughts
- Kerberos has been widely used due to the ticket mechanism it offers.
- It also supports different operating systems such as Microsoft Windows, Apple macOS , Linux.
- Both sides (Client and Server) mutually authenticate each other through the protocol.